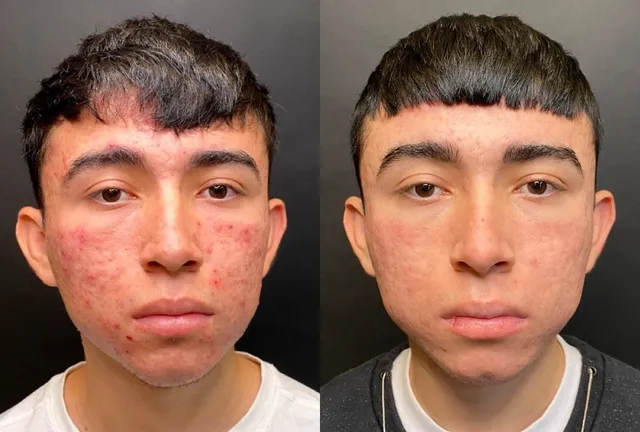
Acne, despite being a common skin condition, can profoundly impact one’s self-esteem and overall well-being. Characterized by blemishes, inflammation, and sometimes scarring, acne affects individuals of all ages and skin types. Understanding the underlying causes of acne and exploring effective treatment options are crucial steps toward achieving clear, radiant skin. Let’s delve into the science of flawless skin by examining the intricacies of acne and unveiling innovative approaches to its treatment.
Understanding Acne
Acne is a multifactorial skin disorder influenced by a combination of genetic, hormonal, environmental, and lifestyle factors. It typically begins during adolescence due to hormonal changes that stimulate the sebaceous glands to produce excess oil. This excess oil, along with dead skin cells and bacteria, can clog hair follicles and lead to the formation of various types of acne lesions, including whiteheads, blackheads, papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts.
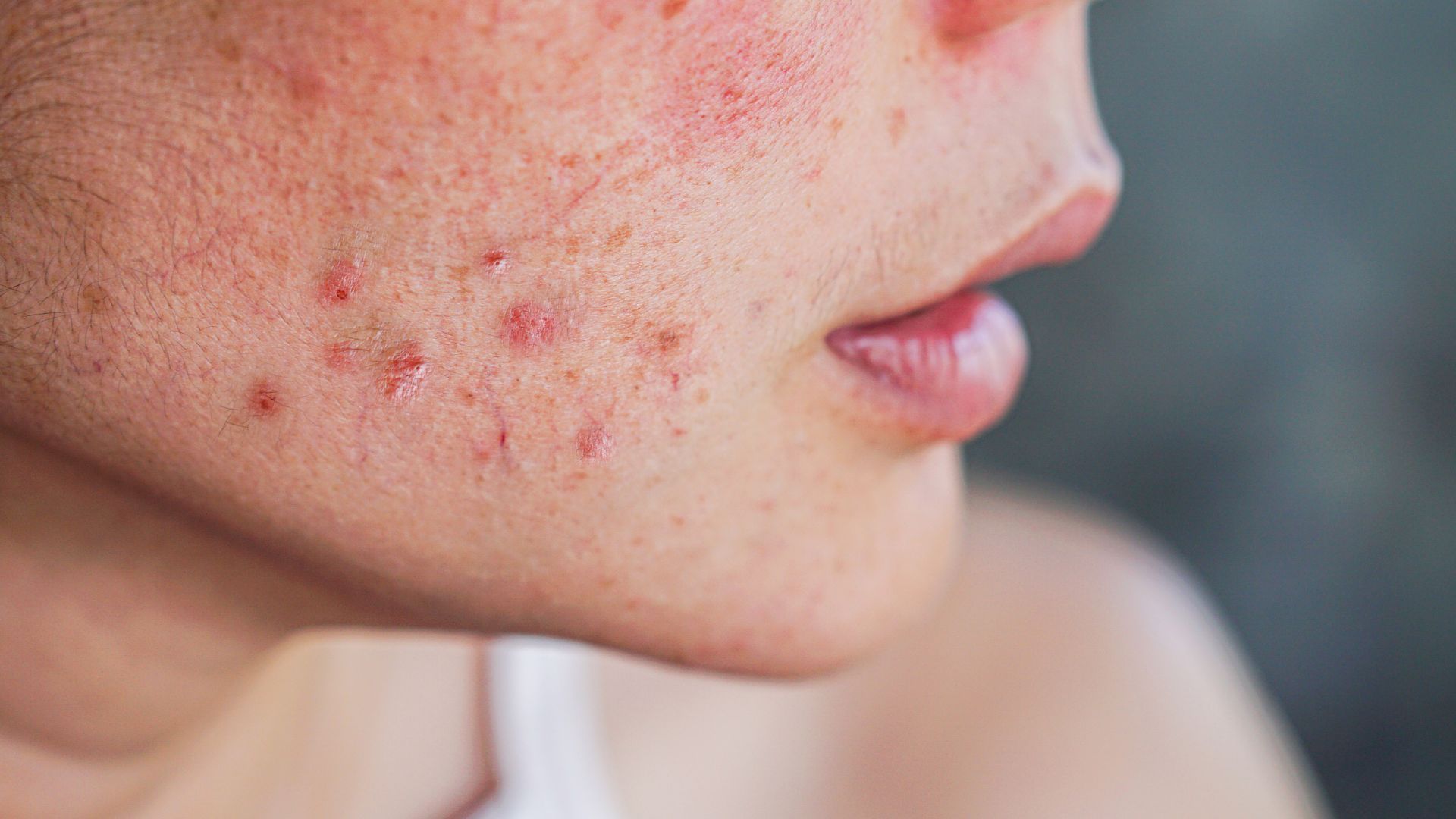
The impact of acne extends beyond its physical manifestations, often causing emotional distress and affecting one’s self-confidence. Common concerns associated with acne include persistent breakouts, inflammation, redness, scarring, and hyperpigmentation. Fortunately, advancements in dermatology have led to a myriad of effective treatments aimed at addressing these concerns and restoring clarity to the skin.
Range of Treatments
Treating acne requires a multifaceted approach tailored to the individual’s specific skin type, severity of acne, and underlying causes. Among the various treatment options available, some of the most effective include topical treatments, oral medications, chemical peels, laser therapy, and photodynamic therapy.
Topical treatments, such as benzoyl peroxide, retinoids, and salicylic acid, work to unclog pores, reduce inflammation, and inhibit the growth of acne-causing bacteria. Oral medications, including antibiotics, oral contraceptives, and isotretinoin, target acne from within by addressing hormonal imbalances, reducing inflammation, and regulating sebum production.
Chemical peels utilize exfoliating agents to remove dead skin cells, unclog pores, and improve overall skin texture and tone. Laser therapy and photodynamic therapy target acne by reducing oil production, killing acne-causing bacteria, and promoting collagen production to improve skin texture and reduce scarring.
Treating acne requires a multifaceted approach tailored to the individual’s specific skin type, severity of acne, and underlying causes. Among the various treatment options available, some of the most effective include topical treatments, oral medications, chemical peels, laser therapy, and photodynamic therapy.
Topical treatments, such as benzoyl peroxide, retinoids, and salicylic acid, unclog pores, reduce inflammation, and inhibit the growth of acne-causing bacteria. Oral medications, including antibiotics, oral contraceptives, and isotretinoin, target acne from within by addressing hormonal imbalances, reducing inflammation, and regulating sebum production.
Chemical peels utilize exfoliating agents to remove dead skin cells, unclog pores, and improve skin texture and tone. Laser therapy and photodynamic therapy target acne by reducing oil production, killing acne-causing bacteria, and promoting collagen production to improve skin texture and reduce scarring.

